Lecture 07
Cluster and cloud computing resources
Today’s Topics
- Google Colab
- Center for High-Throughput Computing (CHTC)
Cluster and cloud computing resources
1. Google Colab
Google Colab provides free cloud-based Jupyter notebooks, with free GPU access. Each session is limited to 12 hours of computation, which should be enough for this class. Colab is useful for quick work, but can be tedious since packages need to be reinstalled each time.
Website: colab.research.google.com
Turn GPU mode, default CPU
To enable GPU acceleration, go to:
Runtime → Change Runtime Type → Hardware Accelerator
Colab comes preloaded with some packages, including PyTorch.
Installing packages
You can install additional packages in a notebook cell using:
!pip install package_name
GitHub
Colab can be directly connected to GitHub or Google Drive.
When you import a notebook from GitHub, save it to Drive, otherwise your changes will not be saved.
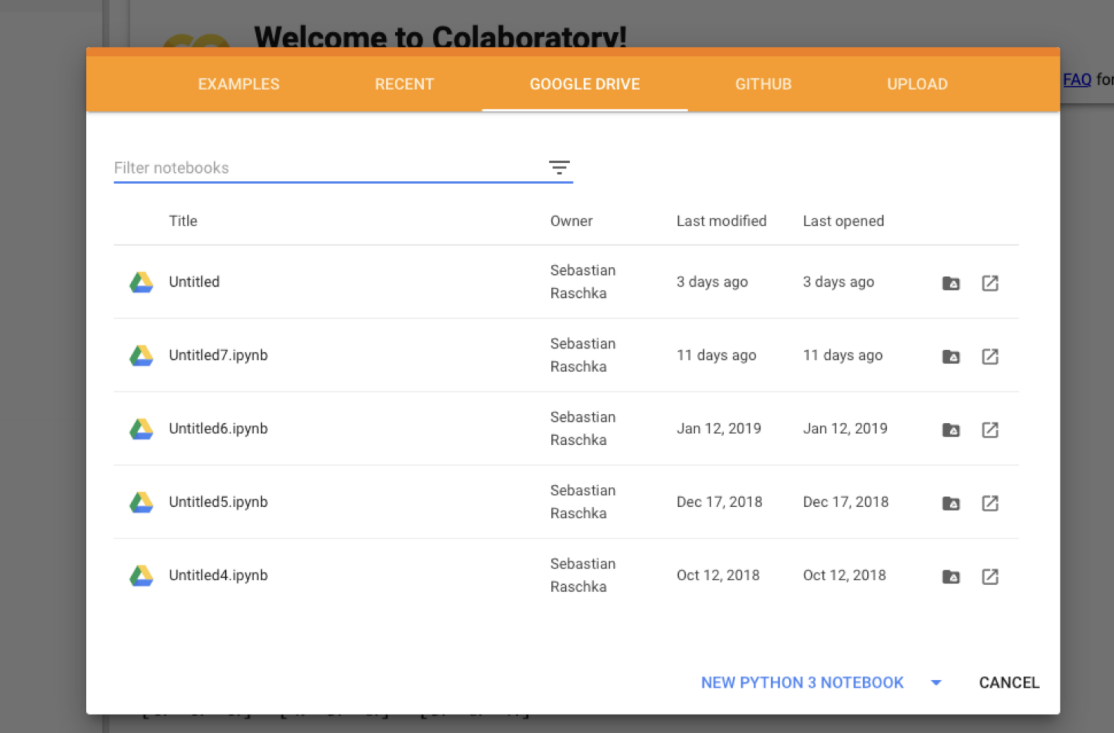
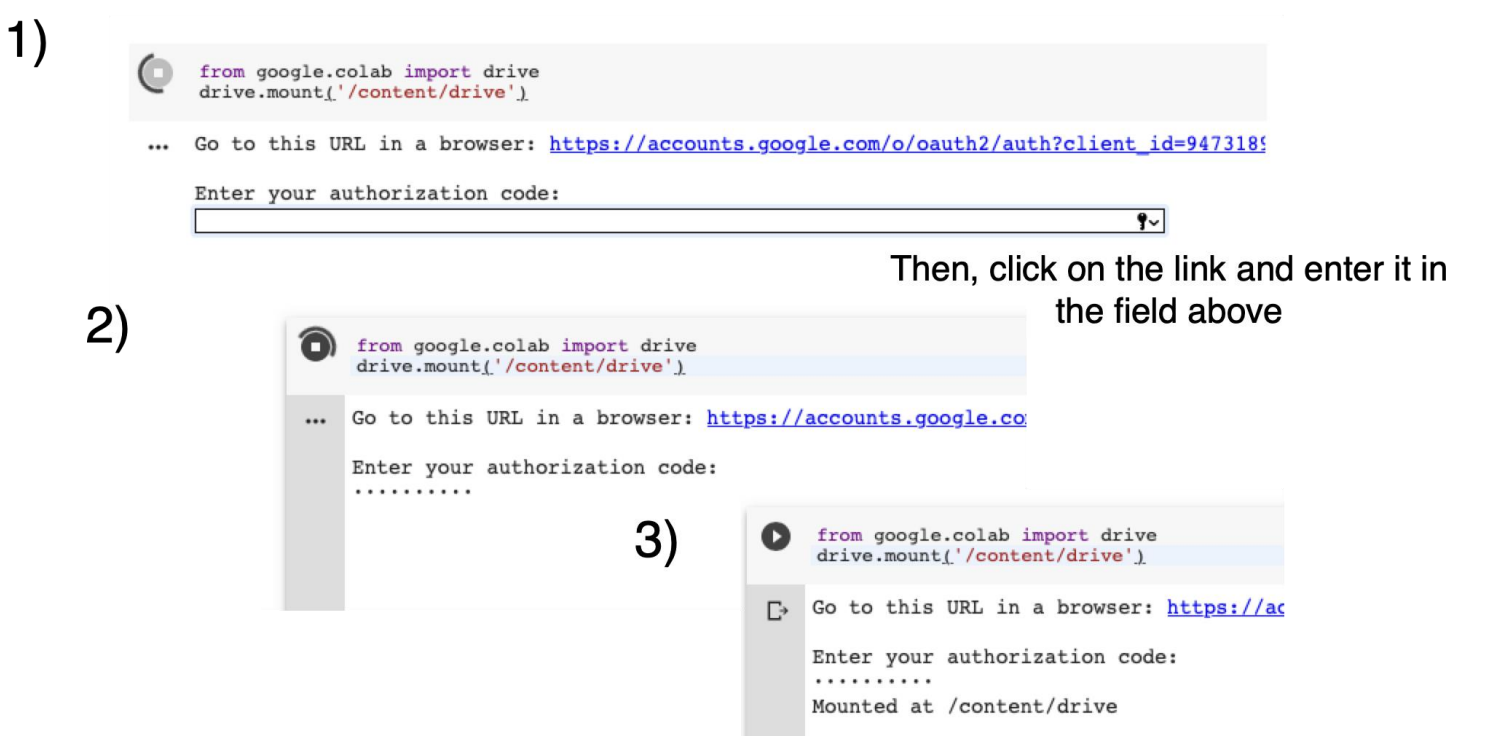
How to get data
Mount your Google Drive to the notebook to access files.
Once mounted, the notebook can open data as usual. Colab does not automatically have access to local data.
Colab is a good way to get free GPU access. There are also many paid vendors for GPU access.
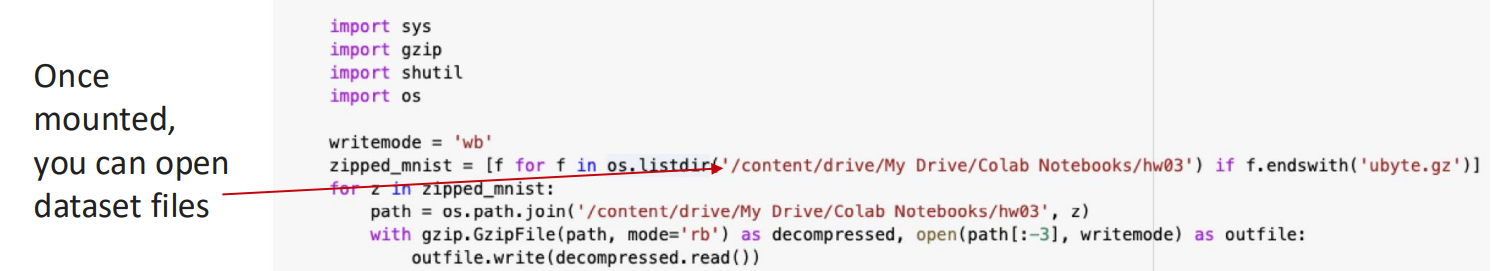
Once mounted, all your Drive files appear under /content/drive/MyDrive/.
You can then open datasets directly from these folders in your Colab notebook.
2. CHTC
CHTC is UW’s own cloud computing server.
If you are working with faculty, you can get a free account and access.
Research is conducted on the use of these servers by UW.
To get access, visit the CHTC website:
- https://chtc.cs.wisc.edu
Click “Request an Account” to apply for access.
People running CHTC are people who make HT condor environment–widely used computing enervionment.